Index
- Guessing Game
- Common Programming Concepts
- Understanding Ownership
- Using Structs
- Enums and Pattern Matching
- Managing Growing Projects with Packages, Crates, and Modules
- Defining Modules to Control Scope and Privacy
- Paths for Referring to an Item in the Module Tree
- Bringing Paths into Scope with the use Keyword
- Separating Modules into Different Files
- Common Collections
- Error Handling
- Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes
- Writing Automated Tests
- Object Oriented Programming
- Adding dependancies
- Option Take
- RefCell
- mem
- Data Structure
- Recipe
- Semi colon
- Calling rust from python
- Default
- Crytocurrency With rust
- Function chaining
- Question Mark Operator
- Tests with println
- lib and bin
- Append vector to hash map
- Random Number
- uuid4
- uwrap and option
- Blockchain with Rust
- Near Protocol
- Actix-web
Guessing Game
Takeaways Keywordsmut
String::new
Reference (&mut)
read_line
parse
Result (Who returns it, Ok, Err)
match, cmp
Ordering (enum)
Shadowing
String::new
Reference (&mut)
read_line
parse
Result (Who returns it, Ok, Err)
match, cmp
Ordering (enum)
Shadowing
use std::io;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
}
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
}
let statement is used to create a variable.In Rust, variables are immutable by default.
The following example shows how to use
mut before the variable name to make a variable mutable.let foo = 5; // immutable
let mut bar = 5; // mutable
let mut bar = 5; // mutable
let mut guess = String::new();
String is a string type provided by the standard library that is a growable, UTF-8 encoded bit of text.
The :: syntax in the ::new line indicates that new is an associated function of the String type. An associated function is implemented on a type, in this case String, rather than on a particular instance of a String. Some languages call this a static method.
To summarize, the
let mut guess = String::new(); line has created a mutable variable that is currently bound to a new, empty instance of a Stringio::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
If we hadn’t put the
use std::io line at the beginning of the program, we could have written this function call as std::io::stdin. The stdin function returns an instance of std::io::Stdin, which is a type that represents a handle to the standard input for your terminal.The
& indicates that this argument is a reference, , which gives you a way to let multiple parts of your code access one piece of data without needing to copy that data into memory multiple times.For now, all you need to know is that like variables, references are immutable by default. Hence, you need to write
&mut guess rather than &guess to make it mutableHandling Potential Failure with the Result Type
.expect("Failed to read line");
read_line puts what the user types into the string we’re passing it, but it also returns a value—in this case, an io::Result. Rust has a number of types named Result in its standard library: a generic Result as well as specific versions for submodules, such as io::ResultThe
Result types are enumerations, often referred to as enums.For
Result, the variants are Ok or Err. The Ok variant indicates the operation was successful, and inside Ok is the successfully generated value. The Err variant means the operation failed, and Err contains information about how or why the operation failed.If you don’t call
expect, the program will compile, but you’ll get a warningRust warns that you haven’t used the
Result value returned from read_line, indicating that the program hasn’t handled a possible error.The right way to suppress the warning is to actually write error handling, but because you just want to crash this program when a problem occurs, you can use
expect println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
#![allow(unused_variables)]
fn main() {
let x = 5;
let y = 10;
println!("x = {} and y = {}", x, y);
}
This code would print
x = 5 and y = 10.[dependencies]
rand = "0.7.3"
rand = "0.7.3"
use std::io;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, 101); // 1. Generate random number
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number); // 2. Print the generate rando number
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
}
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, 101); // 1. Generate random number
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number); // 2. Print the generate rando number
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
}
Ordering
use rand::Rng;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::io;
fn main() {
// --snip--
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::io;
fn main() {
// --snip--
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
The first new bit here is another
use statement, bringing a type called std::cmp::Ordering into scope from the standard library. Like Result, Ordering is another enum, but the variants for Ordering are Less, Greater, and Equal.The
cmp method compares two values and can be called on anything that can be compared.It takes a reference to whatever you want to compare with: here it’s comparing the
guess to the secret_numberA
match expression is made up of arms. An arm consists of a pattern and the code that should be run if the value given to the beginning of the match expression fits that arm’s pattern. Rust takes the value given to match and looks through each arm’s pattern in turn. The match construct and patterns are powerful features in Rust that let you express a variety of situations your code might encounter and make sure that you handle them all.But it gives error due to mismatch types as guess is string:
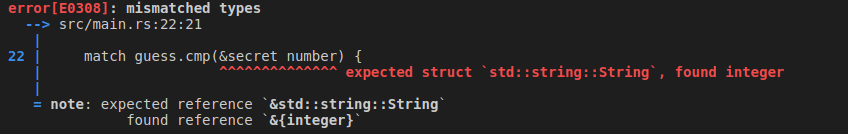
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
We create a variable named
guess. But wait, doesn’t the program already have a variable named guess? It does, but Rust allows us to shadow the previous value of guess with a new one. This feature is often used in situations in which you want to convert a value from one type to another type. Shadowing lets us reuse the guess variable name rather than forcing us to create two unique variables, such as guess_str and guess for example.Although
u32 can contain only numerical characters, the user must press enter to satisfy read_line. When the user presses enter, a newline character is added to the string. For example, if the user types 5 and presses enter, guess looks like this: 5\n. The \n represents “newline,” the result of pressing enter. The trim method eliminates \n, resulting in just 5The parse method on strings parses a string into some kind of number. Because this method can parse a variety of number types, we need to tell Rust the exact number type we want by using let guess: u32.
The colon (
:) after guess tells Rust we’ll annotate the variable’s type.Allowing Multiple Guesses with Looping
// --snip--
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess.");
// --snip--
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
}
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess.");
// --snip--
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}
}
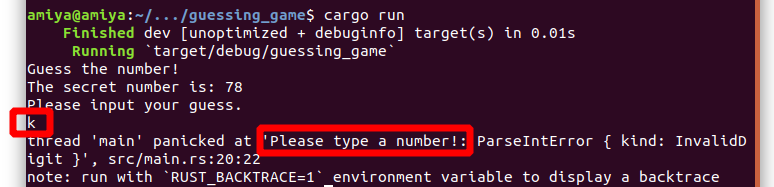
But its a infinite loop, you can interrupt the program with ctrl+c or enter a non number that raises an exception
Quitting After a Correct Guess
// --snip--
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
}
}
}
}
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
}
}
}
}
Handling Invalid Input
Old syntax
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");
// --snip--
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
// --snip--
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
// --snip--
continue, which tells the program to go to the next iteration of the loop and ask for another guess
Remember, parse returns a Result type and Result is an enum that has the variants Ok or Err
use rand::Rng;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::io;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, 101);
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
}
}
}
}
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::io;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1, 101);
println!("The secret number is: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess.");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut guess)
.expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("You guessed: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
}
}
}
}